And systemic circulation the circuit through the rest of the body to provide. Pulmonary Circulation deals solely with the lungs while systemic circulation deals with the rest of the body.
 Systemic Circulation Wiktionary
Systemic Circulation Wiktionary
The cardiovascular system is composed of two circulatory paths.
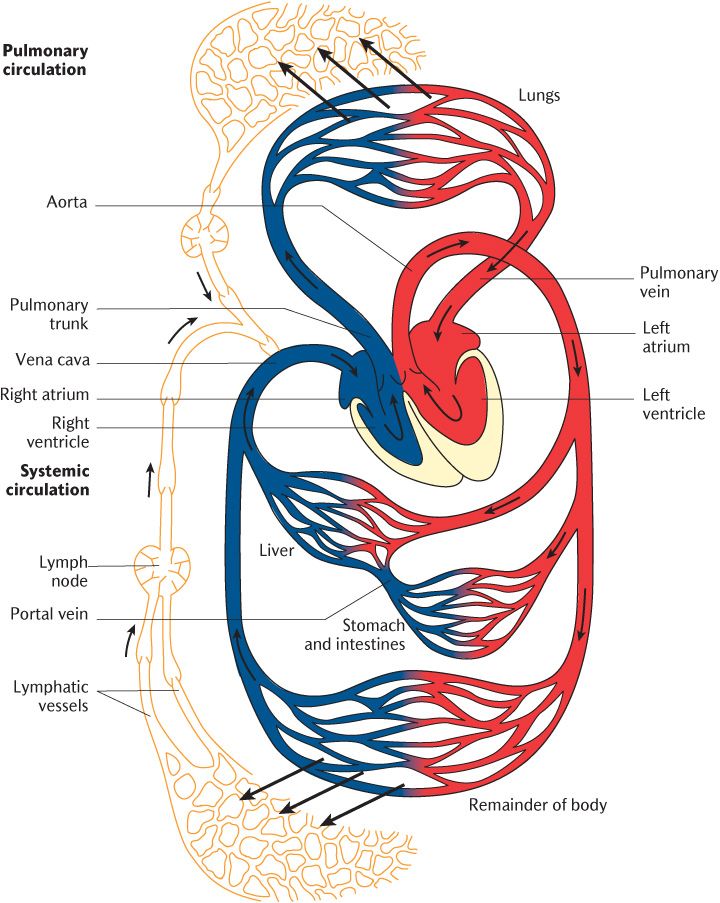
Systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation. Some other circulatory routes which are all subdivisions of systemic circulation include hepatic portal circulation coronary cardiac circulation fetal circulation and the cerebral circulation Systemic circulation The largest route is the systemic circulation. After moving through the pulmonary circuit oxygen-rich blood in the left ventricle leaves the heart via the aorta. The main difference between pulmonary and systematic circulation is that pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs and oxygenated blood back to the heart whereas systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the heart throughout the body and deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Pulmonary and systemic circulation are two separate cardiovascular systems for distributing oxygen -rich blood from the heart and lungs throughout the body. The part of blood circulation that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart. On the evolutionary cycle pulmonary circulation first occurs in lungfishes and amphibians the first animals to acquire a three-chambered heart.
Edapt Systemic Circulation notes Anatomy and Physiology III with Lab-Holsey Unit 3 close The vessels of the circulatory system form a complex network that interacts with all regions of the body. Pulmonary and Systemic Circulations. Systemic and Pulmonary Circulations Differentiate between the different portions of the cardiovascular system.
The oxygenated blood from the lungs returns to the left atrium of the heart through two pulmonary. The place where the blood comes from in your heart is also the main difference. Systemic circulation takes blood from the left ventricle of the heart and in pulmonary circulation blood is taken from the right ventricle of the heart.
Pulmonary circulation the circuit through the lungs where blood is oxygenated. The systemic circulation system is the most commonly. The pulmonary trunk right and left pulmonary artery carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs where the exchange of gases takes place.
Circulatory routes The two basic circulatory routes after birth are systemic and pulmonary circulation. An understanding of the systemic and hepatic portal pathways aids us in identifying different homeostatic imbalances that can occur both in location and cause. Pulmonary circulation systemic circulation and coronary circulation.
Pulmonary Circulation takes deoxygenated blood and converts it back to oxygenated blood while systemic circulation takes the oxygenated blood to the cells and brings back the deoxygenated blood that is released by the cells in the body. The systemic circuit is the path of circulation between the heart and the rest of the body excluding the lungs. The systemic circulatory system circulates oxygenated blood from the heart around the body into the tissues before returning deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Both main pulmonary artery diameter and paa ratio are helpful for diagnosing pulmonary hypertension. Pulmonary circulation - The flow of deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and the return of oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium is called pulmonary circulation. Pulmonary circulation system of blood vessels that forms a closed circuit between the heart and the lungs as distinguished from the systemic circulation between the heart and all other body tissues.
The pulmonary circulatory system circulates deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs via the pulmonary artery and returns it to the heart via the pulmonary vein. This blood is circulated from the aorta to the rest of the body by various major and minor arteries. Systemic Circulation Essay Short essay on Human Circulatory SystemThe systemic circulatory system provides food and nutrients to all the organs tissues and cells in the bodyPulmonary Circulation is a part of the cardiovascular system which is responsible for carrying de-oxygenated from the heart to the lungs and then back to the heart for it to transfer theBlood is the fluid that.
The angioct of the pulmonary arteries to discard pe pulmonary embolism is a common challenge for the general radiologist on call. A diagram of pulmonary. Pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood whereas systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood.
6 rows Pulmonary circulation is mainly responsible for supplying oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide to.
Systemic circulation The blood flow from the left ventricle through the aorta and all its arteries to the capillaries of the tissues and its return to the heart through. Pulmonary circulation systemic circulation and coronary circulation.
 Systemic Circulation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Systemic Circulation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
As outlined above the aorta is.
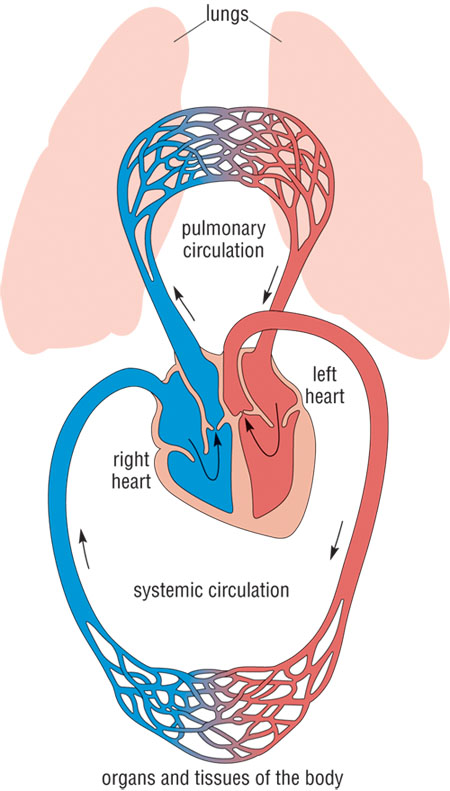
What is systemic circulation. It is responsible for carrying oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body and the deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body back to the heart. Blood is pumped from the left ventricle of the heart through the aorta and arterial branches to. Systemic circulation on the other hand forms a.
This blood is circulated from the aorta to the rest of the body by various major and minor arteries. The blood is then pumped through the mitral valve into the left ventricle. Here is a description of how blood moves through this pathway see the figure.
The pulmonary veins push oxygenated blood into the left atrium. The oxygenated blood from the lungs returns to the left atrium of the heart through pulmonary veins. Systemic circulation is the movement of blood from the heart through the body to provide oxygen and nutrients to the tissues of the body while bringing deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Systemic circulation - circulation that supplies blood to all the body except to the lungs circulation - movement through a circuit. Circulation of blood throughout the body through the arteries capillaries and veins which carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to various tissues and return venous blood. After moving through the pulmonary circuit oxygen-rich blood in the left ventricle leaves the heart via the aorta.
Systemic circulation is a part of the cardiovascular system in many complex organisms including humans. The passage of arterial blood from the left atrium of the heart through the left ventricle the systemic arteries and the capillaries to the organs and tissues that receive much of its oxygen in exchange for carbon dioxide and the return of the carbon-dioxide carrying blood via the systemic veins to enter the right atrium of the heart and to participate in the pulmonary circulation. Systemic and Pulmonary Circulations Differentiate between the different portions of the cardiovascular system.
Especially the movement of blood through the heart and blood vessels. It extends down the length of the chest and abdomen and reaches the pelvis dividing into two branches the iliac arteries see Fig. As outlined above the aorta is the major artery of the systemic circulation.
The systemic circulation is the part of the vascular system that carries blood from the left ventricle to organs and tissues of the body. Systemic circulation in physiology the circuit of vessels supplying oxygenated blood to and returning deoxygenated blood from the tissues of the body as distinguished from the pulmonary circulation. Systemic circulation brings oxygenated blood around to all your bodys cells.
Oxygenated blood enters the left atrium from the pulmonary veins. The systemic circulation is the part of the vascular system that carries blood from the left ventricle to organs and tissues of the body. A diagram of both pulmonary and systemic circulation Pulmonary circulation is a part of the circulatory system responsible for forming a circuit of vessels that transport blood between the heart and the lungs.
This particular system is known as the hepatic portal system although its also sometimes and somewhat inaccurately called the portal venous system. The systemic circuit is the path of circulation between the heart and the rest of the body excluding the lungs. When the left atrium relaxes the oxygenated blood drains into.
The systemic circulation is the circulation system that carries oxygenated blood throughout the body and returns the deoxygenated blood to the heart from the body tissues. The term is most often used to refer to how blood moves through the network of veins in the gut and digestive organs such as the spleen and pancreas and is carried to the liver.