Is the process by which the nucleus of the cell is divided into two nuclei each with the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the parent cell. Cytokinesis is the second stage.
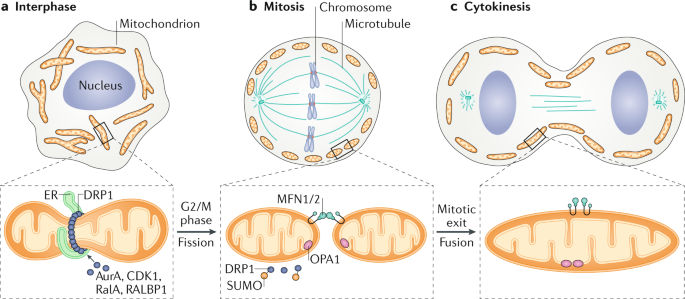 Membrane And Organelle Dynamics During Cell Division Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
Membrane And Organelle Dynamics During Cell Division Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
In the nucleus the chromosomes are duplicated but are not yet distinguishable because they are still a form of chromatin.

Cell division mitosis and cytokinesis. It begins prior to the end of mitosis in anaphase and completes shortly after telophasemitosis. There are two types of cell division. While there are several differences between them the two overlap during cell division.
The growth and development of an individual depends exclusively on the growth and multiplication of the cells. There are two types of organisms-acellular and multicellular. Thus the goal of mitosis and cytokinesis is now complete because one parent cell has given rise to two daughter cells.
Mitosis cytokinesis and the cell cycle. Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division during which the cytoplasm splits into two and two daughter cells form. Begins abruptly as the centromeres of the chromosomes split simultaneously.
They are located at the tips of roots shoots and in the stem between the xylem and phloem. Cell division in animals. Links Back to Top Access Excellence page on Mitosis.
In animal cells the plasma membrane of the parent cell pinches inward along the cells equator until two daughter cells form. Normal cell division in all cells except germ cells occurs by 2 mechanical processes that initially divide the nucleus then the cell cytoplasm. Mitosis and cytokinesis are both part of cell division.
One may also ask which types of cells divide. The cell cycle can be described in several ways. Mitosis and cytokinesis are two different processes that occur in the cell division cycle.
Process by which the cytoplasm divides thus forming two. Cell is ready to divide Mitosis Division of the nucleus where the cell forms two genetically identical cells. Nuclear division among multicellular organisms is of two types.
These are diploid cells with each cell containing a full complement of chromosomes. The two centrosomes are on opposite poles of the cell then cluster at the middle of the cell with their centromeres precisely aligned at the equator of the spindle. Cell division in eukaryotic cells includes mitosis in which the nucleus divides and cytokinesis in which the cytoplasm divides and daughter cells form.
Karyokinesis or mitosis is divided into five stagesprophase prometaphase metaphase anaphase and telophase. Breaking it into G1 S G2 and M phases emphasizes patterns in DNA replication and separation. The mitosis division process has several steps or phases of the cell cycleinterphase prophase prometaphase metaphase anaphase telophase and cytokinesisto successfully make the new diploid cells.
The division of eukaryotic cells occurs in two main stages. Mitosis occurs in four phases called prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. In plants the phragmoplast extends and forms the cell wall.
In Cytokinesis the contractile ring in animal cells contracts and pinches the cell into 2 daughter cells. Mitosis and cytokinesis occur at the end of the cell cycle as the single cell divides to form two genetically identical copies. In plants mitosis occurs only in the meristem tissues.
Cytokinesis is the division of the cells cytoplasm. Cytokinesis is the process of splitting the daughter cells apart. Which divides the cytoplasm organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components.
Basically Mitosis is a process by which the duplicated genome in a cell is separated into halves that are identical in nature. Phase of interphase where the cell is growing and organelles are doubling. Both Mitosis and Cytokinesis are a part of cell division.
It was Virchow who first of all adequately stated the cell division. The term mitosis refers to the nuclear division stages prophase prometaphase metaphase anaphase and telophase of the cell cycle. Meiosis meanwhile is involved in generating four haploid sex cells called gametes that are used for sexual reproduction.
Mitosis is the first stage. Mitosis which is associated with repair and growth of the organism is the process of producing two identical diploid daughter cells. Third and shortest phase.
Cell division in animals is a two-step process involving mitosis and cytokinesis and is set up by interphase. There are other subtle differences between the two. During cytokinesis the cytoplasm splits in two and the cell divides as shown below.
Generally mitosis is similar to karyokinesis given that it involves division of the cell nucleus. Cytokinesis is the process where the cytoplasm of the cell divides to form two daughter cells. Interphase is a growth period for the cell.
At the end of cytokinesis two genetically identical daughter cells are produced. The mitosis cell cycle includes several phases that. This process produces two daughter cells that should be genetically identical to the parent cell.
Whereas mitosis is the division of the nucleus cytokinesis is the splitting of the cytoplasm and allocation of the golgi plastids and cytoplasm into each new cell. In general mitosis division of the nucleus is preceded by the S stage of interphase during which the DNA is replicated and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis.