The distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell of the electron is known as the atomic radius of an element. Valence shell orbital radii for potassium.
 10 12 Review What Is Atomic Radius
10 12 Review What Is Atomic Radius
Although neither atoms nor ions have sharp boundaries they are sometimes treated as if they were hard spheres with radii such that the sum of ionic radii of the cation and anion gives the distance between the ions in a crystal latticeIonic radii are typically given in units of either picometers pm or.

Atomic radius of potassium. The radius of potassium atom is 0. Vital to function of nerve and muscle tissures. It must be noted atoms lack a.
7 Zeilen The atomic radius of Potassium atom is 203pm covalent radius. The observations are interpreted with coupled cluster. This is due to it losing one electron so its outermost shell could be full.
Atomic Radius Comparison Ion and Neutral Comparison. The size of an atom is independent of the number of the number protons in the nucleus the number of energy levels holding electrons and the number of electrons in the outer energy level. The electronic configuration of Potassium is Ar4s 1.
In the solid state Potassium has a body-centered cubic crystal structure with a 0533 nm and a nearest neighbor distance of 0277 nm. Also as saltpeter potassium nitrate KNO3 to make explosives and to color fireworks in mauve. Ionic Radius Potassium Periodic Trend.
Its atomic radius is 0235 nm and the 1 ionic radius is 0133 nm. Atomic Mass 390983 Learn more about the atomic mass. Beryllium is a chemical element with atomic.
2 0 3 nm. Atomic radius of Cerium. Orbital Radius pm Radius AU.
Its atomic radius is 0235 nm and the 1 ionic radius is 0133 nm. The atomic radius decreases rightward along each period row of the table due to the increase in effective nuclear charge the charge of the. Oxygen carbon aluminum potassium Explanation.
That means it lost an entire shell. The radius of the potassium ion in nano-meter will be. The elements in increasing order of atomic radius.
If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. Ionic radius r ion is the radius of a monatomic ion in an ionic crystal structure. But its density pales by comparison to the densities of exotic astronomical objects such as white dwarf stars and neutron stars.
The ion of potassium is going to have a smaller radius compared to the neutral element. Formerly called kalium K. Europium is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air and water.
119 Zeilen Atomic radius of Lanthanum. Potassium Data Potassium Atomic Radius 277 Å State at 20 C Solid Uses Used as potash in making glass soap. Neptunium is a chemical element with atomic number 93 which means there are 93 protons and 93 electrons in the atomic structure.
The charge radii of potassium isotopes up to 52K are measured and show no sign of magicity at 32 neutrons as previously suggested in calcium. Potassium 2882 As we can see only Potassium has four electron shells.
John Daltons atomic model. List of Atomic Theories 1.
 Atomic Theory Timeline Scientists Atomic Theory Chemistry Projects Atom
Atomic Theory Timeline Scientists Atomic Theory Chemistry Projects Atom
Another century passed before the theory was universally accepted by scientists.

When was the atomic theory discovered. Democritus defined his take on what would later become atomic theory by starting with a stone. It provided a physical. According to the Thomson atomic model often referred to as the plum-pudding model the atom is a sphere of uniformly distributed positive charge about one angstrom in diameter.
As he put it if you were to divide a stone it would be two smaller stones. He also suggested that the nuclei of elements other than hydrogen must contain electrically neutral particles with approximately the same mass as the proton. John Dalton was a English chemist best known for his work on modern atomic theory and his research about color blindness.
Between 1903 and 1907 Thomson tried to solve the mystery by adapting an atomic model that had been first proposed by Scottish scientist William Thomson Lord Kelvin in 1902. 370 BC a Greek philosopher developed and systematized classical atomism a theory credited to his teacher Leucippus. Furthermore when did John Dalton discover the atomic theory.
This can be observed with a microscope for any small particles in a fluid. Part II 1810 was the first application of atomic theory to chemistry. The Ancient Greek theory has been credited to several different scholars but is most often attributed to Democritus 460370 BC and his mentor Leucippus.
The neutron however was not discovered until 1932 when James Chadwick 18911974 a student of Rutherford. He proposed that carbon atoms were tetravalent and could bond to themselves to form the carbon skeletons of organic molecules. Though their ideas about atoms were rudimentary compared to our concepts today they outlined the idea that everything is made of atoms invisible and indivisible spheres of matter of infinite type and number.
What are the 5 atomic models. He proposed the Atomic Theory in 1803 which stated that all matter is composed of small particles called atoms. English chemist John Dalton subsequently made on the Greek notion of atoms in 1808.
As a result of Rutherfords work it. Dalton proposed his atomic theory in 1808. In 1827 he noticed that tiny pollen grains suspended in still water moved about in complex paths.
It took until the end of the 18th century for science to provide concrete evidence of the. English chemist and physicist John Dalton extended Prousts work and converted the atomic philosophy of the Greeks into a scientific theory between 1803 and 1808. He called this the theory of the universe.
In two papers outlining his theory of atomicity of the elements 185758 Friedrich August Kekulé was the first to offer a theory of how every atom in an organic molecule was bonded to every other atom. Nobel Prize in Physics 1935 discovered it. Atom - Atom - The beginnings of modern atomic theory.
His research on color blindness is sometimes referred to as Daltonism. The ancient Greek philosophers Democritus and Leucippus recorded the concept of the atomos an indivisible building block of matter as early as the 5th century BCE. In fact the initial theory of the atom was first recorded by the Greek scientist and philosopher Democritus all the way back in 440 BC.
The idea of an indivisible particle was further elaborated upon and explored by a number of scientists and philosophers including Galileo Newton Boyle Lavoisier and Dalton. The theory postulated a world made up of hard indivisible hence atomic from Greek atoma uncuttable particles of matter moving through empty space. Plum Pudding Model and.
In addition they tell that these were solid particles without internal structure and came in. Subsequently question is when was the atomic model developed. Atomic theory originated as a philosophical concept in ancient India.
It is a theory of the nature of matter which it claims is made up of small particles called atoms. Although the atomic theory of matter in its various forms existed a good two thousand years before the time of John Dalton he was the first to propose in his 1808 book A New System of Chemical Philosophy that atoms had weight. Atomic theory began thousands of years ago as a philosophical concept and it was in the 19th century when it achieved widespread scientific acceptance thanks to discoveries in the stoichiometry field.
A Brief History of Atomic Theory The Atom and Atomism. His book A New System of Chemical Philosophy Part I 1808. In 1913 the Danish physicist Niels Henrik David Bohr 1885-1962 together with Ernest Rutherford proposed a model of the atom in which the electrons in an atom were in orbit around its nucleus in much the same way that the planets in our solar system are in orbit around the Sun.
The first truly direct evidence of atoms is credited to Robert Brown a Scottish botanist. All matter consists of atoms which are bits of matter too small to be seen. There is an empty space between atoms Atoms are completely solid Atoms have no internal structure Each atom of a different substance is different in size weight and shape.
To know more differences download BYJUS the learning app. In this case you use the atomic mass in calculations rather than the atomic weight.
What Is The Difference Between Atomic Mass And Atomic Weight Quora
Atomic mass vs Atomic number.

Atomic mass vs atomic weight. If you find an element that exists as only one isotope then the atomic mass and the atomic weight will be the same. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. Atoms of the same element with varying atomic masses.
When it comes to differentiating atomic mass versus atomic weight much of the confusion tends to come from the fact that atomic weight is measured in amu atomic mass units instead of being measured in newtons. One is the average weight of an element and the other is the total number of nucleons in the atoms nucleus. In this section carefully compare.
Atomic mass is the weighted average mass of an atom of an element based on the relative natural abundance of that elements isotopes. Although this may be confusing there is a simple explanation. Definition of Atomic Mass Atomic mass is defined as the number of protons and neutrons contained in an individual unit of a substance.
Due to different numbers of neutrons. A B and C. Atomic mass is used to show different isotopes of the same element.
Can Atomic Mass and Atomic Weight Ever Be the Same. Equals MASS number which is the sum of protons and neutrons. The difference is that one is a count of the protons in an elements nucleus while the other is a count of both the protons and neutrons.
It is atomic mass. Roughly equal to the atomic mass. Atomic mass and atomic weight may equal each other whenever you are working with a single isotope of an element too.
Atomic mass also atomic weight is the total weight of an element. Element Q consists of three different isotopes. The key difference between atomic mass and molecular weight is that the atomic mass is the mass of a single atom whereas the molecular weight is the sum of the weights of the atoms in the molecule.
While the atomic weight is a constant for a given element and is reported in the Periodic Table the atomic mass or mass number varies from one isotope to another. To understand the importance well take a look at the standard definitions of mass. What is the difference between atomic mass and atomic number.
See the case of chlorine where atomic weight and standard atomic weight are about 3545. Isotope A has an atomic mass of 40 amu and accounts for 60 of naturally occurring Q. In other places in the text the author refers to the average atomic mass as.
Atomic mass and mass number which are essentially synonymous and atomic weight. Atomic Weight vs. Atomic mass is the mass of an atom whereas atomic weight is the weighted average of the naturally occurring isotopes.
Also represents the mass of one mole of the element in grams. The major difference between atomic mass and atomic weight is atomic mass is a whole number value whereas atomic weight may or may not be a whole number value. Whats the Difference between Mass Number and Atomic Weight.
Atomic mass is also known as atomic weight. Isotopes B has an atomic mass of 44 amu and accounts for 25 of Q. October 25 2011 Posted by Madhu.
Most people use the terms atomic mass and atomic weight interchangeably. Key Differences between Atomic Mass and Atomic Number Atomic number is represented by Z whereas Atomic mass is represented by A. What is properly called the atomic weight is referred to as the average atomic mass and is given the unit amu Thus the atomic weight of copper is listed as 6355 amu.
Atomic mass does not define the type of element whereas Atomic number defines the type of element. The WEIGHTed average of the different isotopes of an atom. So again the mnemonic for memorizing the difference between atomic mass and atomic weight is.
There are a few different terms used by chemists to describe the heaviness of an element. One difference between atomic mass and molar mass to take note of is that the latter refers to the weight of a mole of a substance while the latter refers to the weight of the molecules of a substance. An atom has weight.
For non-mononuclidic elements that have more than one common isotope the numerical difference in relative atomic mass atomic weight from even the most common relative isotopic mass can be half a mass unit or more eg. The key difference between atomic weight and atomic mass is that atomic weight is the average weight of an element with respect to all its isotopes and their relative abundances but atomic mass is the mass of a single atom. Videos you watch may be.
Atoms are the building blocks of all matter. It is found by adding together the number of protons and neutrons in the.
The standard unit of atomic mass is the unified mass unit. These relative atomic masses were based on the stoichiometric proportions of chemical.
 Define The Atomic Mass Unit Science Atoms And Molecules 13231495 Meritnation Com
Define The Atomic Mass Unit Science Atoms And Molecules 13231495 Meritnation Com
Each unique atom has a unique atomic number and atomic mass.
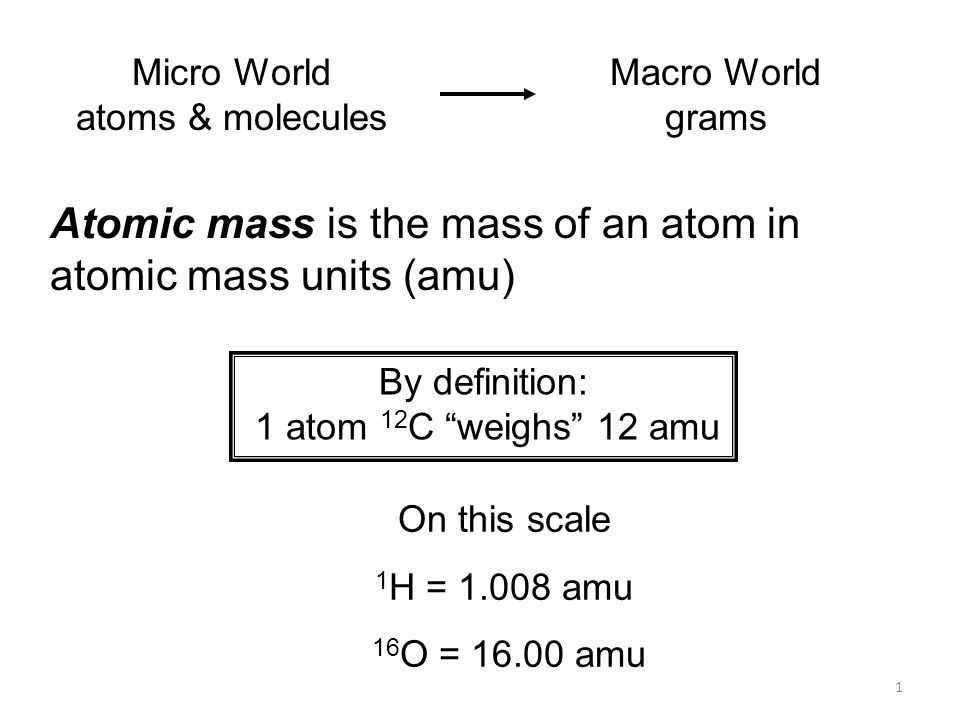
Atomic mass units definition. Atomic mass unit definition a unit of mass equal to 112 00833 the mass of the carbon-12 atom and used to express the mass of atomic and subatomic particles. VIDYA EDUCATIONAL ACADEMY NashikTopic - Atomic Mass Unit Mass defect Binding Energy Stability of Nucleolus Definition of RadioactivityFor. One unified mass unit or one dalton is equal to one-twelfth of the mass of a neutral and unbound atom of isotopic carbon-12 at the ground state.
Atomic Mass Unit AMU The periodic table of elements contains every atom known to mankind. 1 u has a value of 1660 539 066 60 50 10 27 kg. A3002 Massenspektrometer soweit nicht in Nummer 3A233 oder Unternummer 0B002g erfasst für die Messung von Ionen einer Atommasse größergleich 200 amu atomic mass units mit einer Auflösung besser als 2 amu bei 2 00 amu od er.
It is denoted as u. Instead atomic mass is expressed in unified atomic mass units unit symbol. In chemistry an atomic mass unit or AMU is a physical constant equal to one-twelfth of the mass of an unbound atom of carbon -12.
Auf dieser Seite dreht sich alles um das Akronym von AMU und seine Bedeutung als Atomare Masseneinheit. The history of the mole is intertwined with that of molecular mass atomic mass units and the Avogadro number. Bedeutungen von AMU im Englischen Wie oben erwähnt wird AMU als Akronym in Textnachrichten verwendet um Atomare Masseneinheit darzustellen.
It is a unit of mass used to express atomic masses and molecular masses. Also known as the atomic unit of mass In Hartree atomic units the speed of light is approximately 137036 atomic units of velocity. A carbon-12 atom has a mass of 12 u.
In terms of energy 1 amu equals 93149432 MeV. Medical Definition of atomic mass unit. Bitte beachten Sie dass Atomare Masseneinheit nicht die einzige Bedeutung von AMU ist.
It is expressed as a multiple of one-twelfth the mass of the carbon-12 atom 1992646547 10 23 gram which is assigned an atomic mass of 12 units. In this scale 1 atomic mass unit amu corresponds to 1660539040. 1 atomic mass unit is defined as 112 of the mass of a single carbon-12 atom.
Atomic mass unit amu a unit of mass equal by definition to 112 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12 which equals 16605402 10 -27 kg. Atomic units are often abbreviated au or au not to be confused with the same abbreviation used also for astronomical units arbitrary units and absorbance units in. Continuation of Average Atomic Mass and definition of atomic mass unit About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test.
The first table of standard atomic weight atomic mass was published by John Dalton 17661844 in 1805 based on a system in which the relative atomic mass of hydrogen was defined as 1. Atomic mass the quantity of matter contained in an atom of an element. A unit of mass for expressing masses of atoms molecules or nuclear particles equal to ¹₁₂ the mass of a single atom of the most abundant carbon isotope 12C called also dalton Comments on atomic mass unit.
The atomic number is the number of protons. The unified mass unit is also known as the dalton named after John Dalton who known for his atomic theory.